When building computer vision systems, efficient data storage is a fundamental requirement. Whether you're capturing images for training, storing inference results for validation, or archiving sensor data for future analysis, your storage solution must be both reliable and high-performance.
Ingestion speed is especially critical. If your system can’t write data fast enough — whether it’s high-frequency frames or accompanying metadata — you risk losing valuable information or creating bottlenecks in the pipeline.
In this post, we’ll look at three common approaches to storing data in computer vision applications: a traditional file system, S3-compatible object storage, and ReductStore, a time-series-optimized blob storage. We’ll explore the strengths and limitations of each approach to help you choose the best fit for your application.
A Simple Computer Vision Application
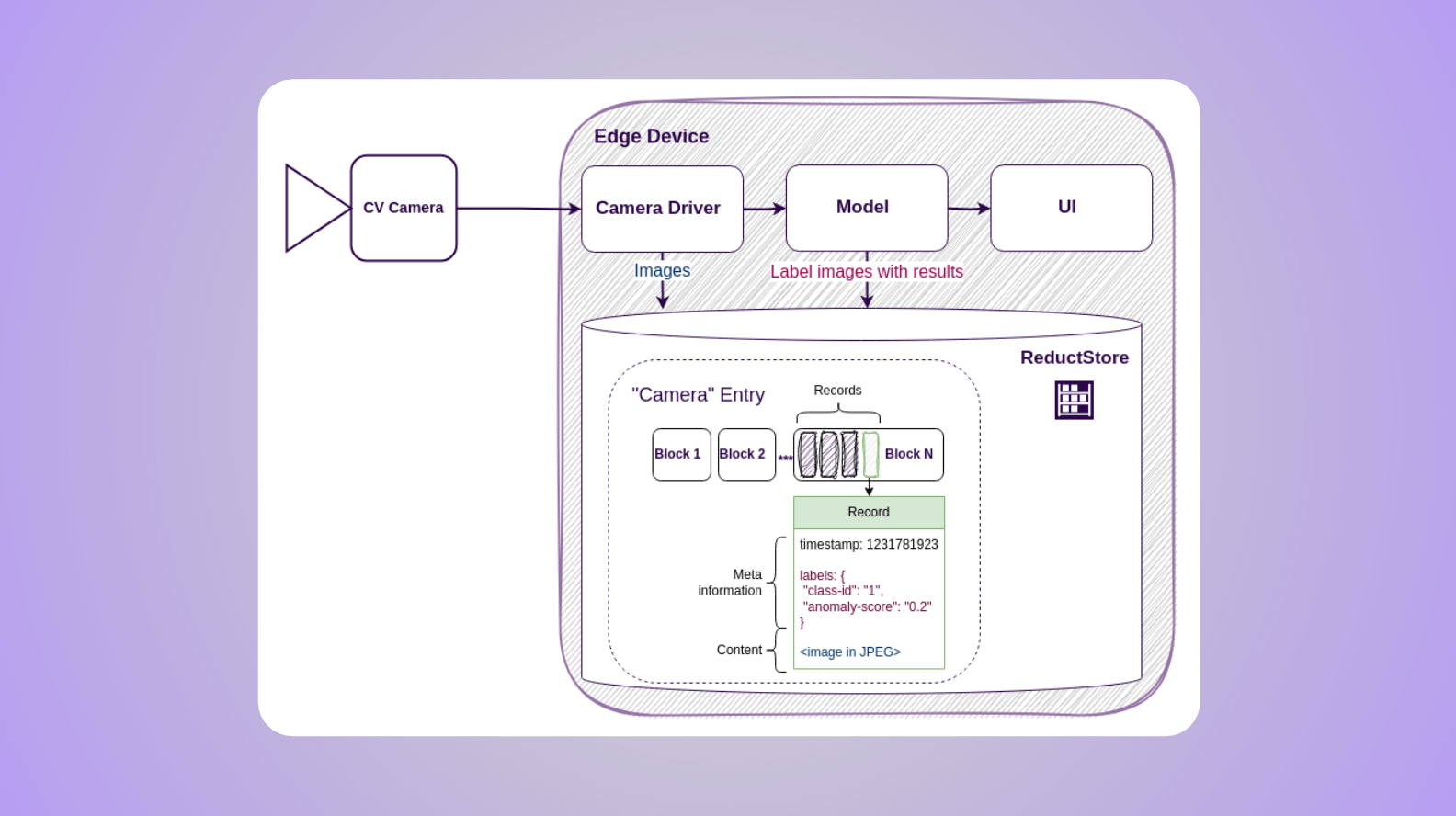
For demonstration purposes, we’ll use a simple computer vision (CV) application which is connected to a CV camera and runs on an edge device:
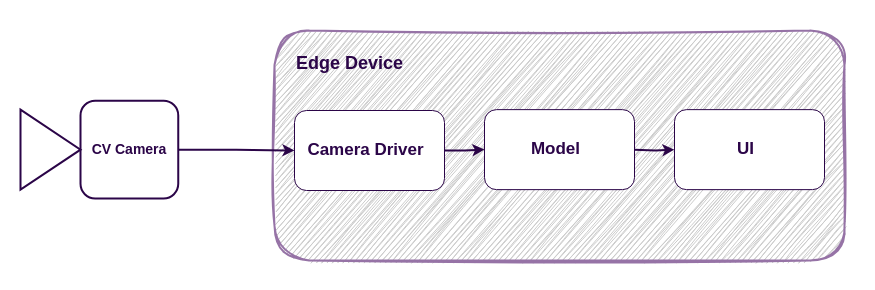
The camera driver captures images from the CV camera every second and forwards them to the model, which then detects objects and displays the results in the user interface.
Your images and results need to be stored for training and validation purposes. The customer may also wish to view images featuring anomalous objects. These requirements present the challenge of maintaining a history of blob or unstructured data.